How Often Are Weather Forecasts Updated
How Reliable Are Weather condition Forecasts?
The Short Respond:
A seven-solar day forecast can accurately predict the weather most 80 percentage of the fourth dimension and a 5-day forecast tin accurately predict the weather approximately 90 percent of the time. However, a x-day—or longer—forecast is but right about half the time.

A weather forecast tin can pretty reliably tell y'all whether or non you'll demand an umbrella tomorrow. Credit: Public Domain Image
If you want to know what the weather will be like within the next week, a atmospheric condition forecast can give you lot a really skilful idea of what to await. A seven-day forecast can accurately predict the weather about lxxx pct of the time and a five-day forecast tin can accurately predict the weather approximately xc percent of the fourth dimension.
However, a 10-twenty-four hours—or longer—forecast is simply correct about half the time. Meteorologists use computer programs called weather models to make forecasts. Since we can't collect data from the future, models have to employ estimates and assumptions to predict futurity atmospheric condition. The atmosphere is changing all the time, so those estimates are less reliable the further you get into the future.

A seven-day forecast is fairly accurate, but forecasts beyond that range are less reliable.
How Weather Forecasts Are Made
Some of the information needed to make a atmospheric condition forecast comes from environmental satellites. NOAA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, operates three types of ecology satellites that monitor Earth'due south weather:
Geostationary satellites: NOAA'south Geostationary Environmental Operational Satellite-R (GOES-R) series satellites orbit approximately 22,000 miles higher up Earth and they provide a flick of what the weather is like correct now. "Geostationary" means that the satellites orbit at the same charge per unit that the Earth rotates. This means they can collect nearly-continuous images over the same area. Because they focus on one spot, they tin provide upwards-to-the-minute data nearly astringent weather. This information helps forecasters sympathize how rapidly a storm, such equally a hurricane, is growing and moving.
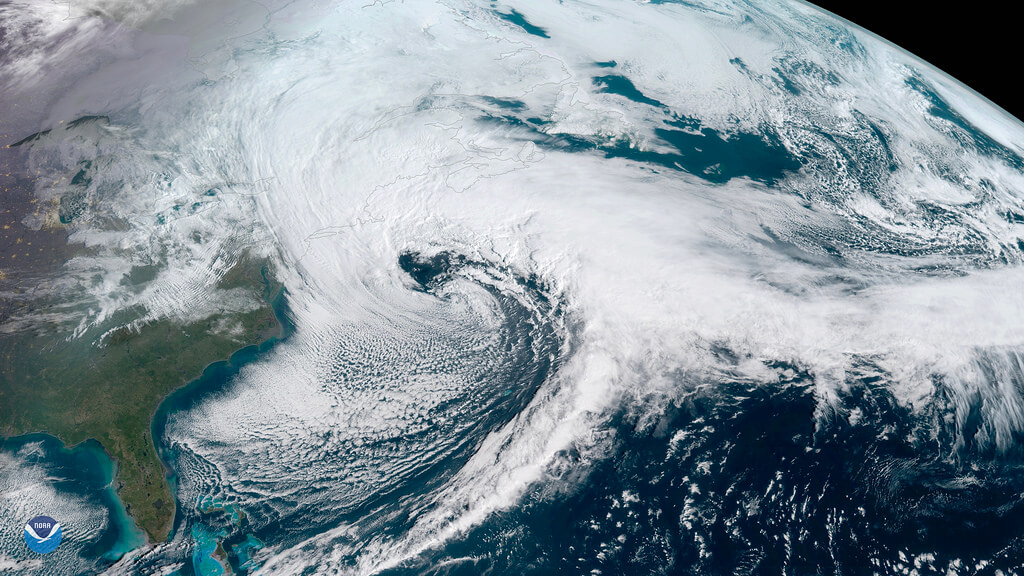

An image of a Nor'easter off the declension of New England captured by a NOAA geostationary satellite called GOES-East. Credit: NOAA
Polar-orbiting satellites: Satellites equally part of NOAA'south Joint Polar Satellite Organization (JPSS) orbit approximately 500 miles above Earth. They zippo around our planet from pole to pole 14 times per day. Because they orbit while the World is rotating below, these satellites can see every office of Earth twice each day. Polar orbiting satellites can monitor the entire Globe'south atmosphere, clouds and oceans at high resolution. Past watching these global weather patterns, polar orbiting satellites tin help meteorologists accurately predict long-term forecasts—up to 7 days in the future.
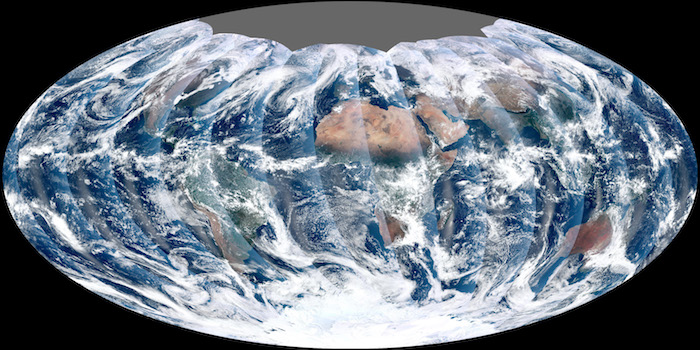
Polar orbiting satellites go a consummate view of Earth each 24-hour interval by orbiting from pole to pole. Because the Earth spins, the satellite sees a dissimilar role of Globe with each orbit. It captures a picture of the entire planet as a serial of wedges that then be pieced back together, as in the image above. Credit: NASA'southward NPP Land Production Evaluation and Testing Element
Deep infinite satellite: NOAA's Deep Space Climate Observatory (DSCOVR) orbits one million miles from World. Information technology provides space weather alerts and forecasts while also monitoring the amounts of solar free energy absorbed by Earth every day. DSCOVR too makes observations about ozone and aerosols in World's atmosphere. These factors are of import in making air quality forecasts.
Polar orbiting satellites provide the information most useful for long-term weather forecasting. These satellites use instruments to mensurate energy, chosen radiation, emitted by the Earth and temper. This information is incorporated into weather models, which in plow leads to more accurate atmospheric condition forecasts. Other instruments can also be used to map bounding main surface temperature—an important factor in long-term weather forecasting.
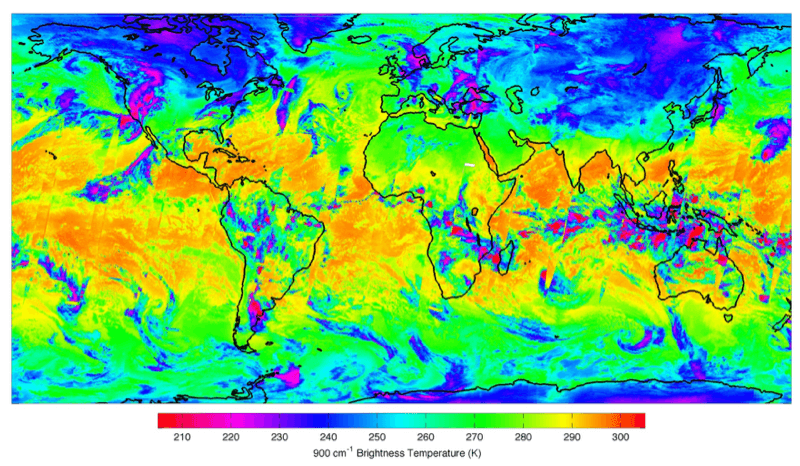
Polar orbiting satellites monitor the whole Globe. This map, created with data from a polar orbiting satellite called Suomi-NPP, shows warm sea surface temperatures in orange and cold temperatures and loftier cloud tops in magenta. This information is important for long-term forecasting. Credit: NOAA
The satellite performs these accurate measurements all around the globe twice per twenty-four hours. This flood of data is what helps weather forecasters to reliably predict the weather up to 7 days in advance. These measurements can also help forecasters predict seasonal conditions patterns, such every bit El Niño and La Niña.
Polar orbiting satellites collect essential information for the models that forecast severe atmospheric condition like hurricanes, tornadoes and blizzards days in advance. The information they collect is as well needed to assess environmental hazards such as droughts, woods fires, poor air quality, and harmful coastal waters.
Source: https://scijinks.gov/forecast-reliability/
Posted by: cotnerfolearribled.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How Often Are Weather Forecasts Updated"
Post a Comment